Antimicrobial Resistance
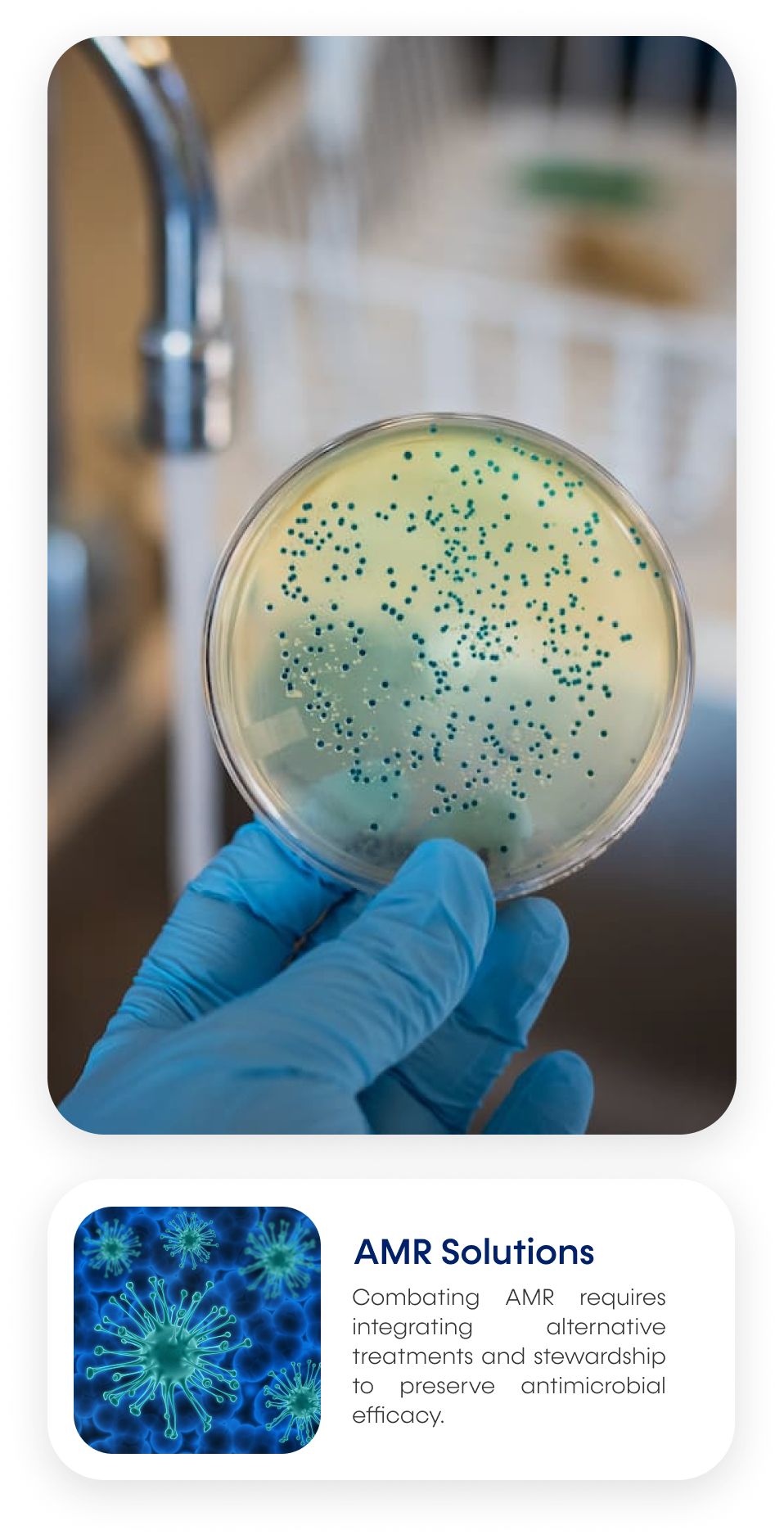
ICOH aims to understand better the nexus of AMR transfer across humans, animals and ecosystems. Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR) occurs when microorganisms develop resistance to drugs, reducing the effectiveness of antibiotics and posing a serious global public health threat.